What is photocatalyst ?
1 History of photocatalyst
2 Theory of photocatalyst
3 Application of photocatalyst
1. History of photocatalyst
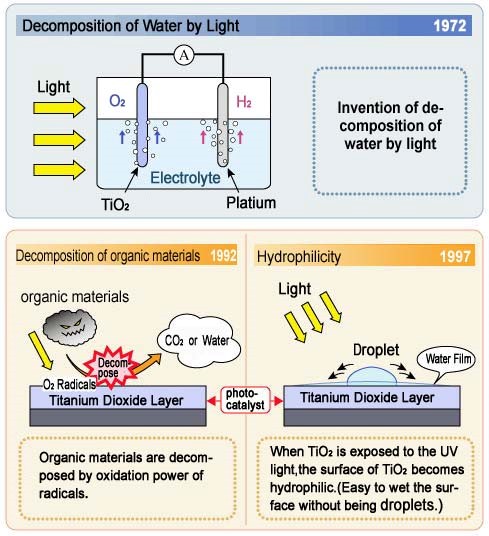
Basic theory of photocatalyst was invented by Japanese chemists in1972.
They invented that water decomposed only by light(UV) using TiO2 & platinum electrodes. In 1992, coating method of TiO2(Titanium dioxide) was developed. And it was found that organic materials were decomposed by radicals coming from photo catalyst reaction. In 1997, hydrophilicity of photocatalyst was invented. All of these inventions were done in Japan and it is said photocatalyst is a technology from Japan.
2.Theory of photocatalyst
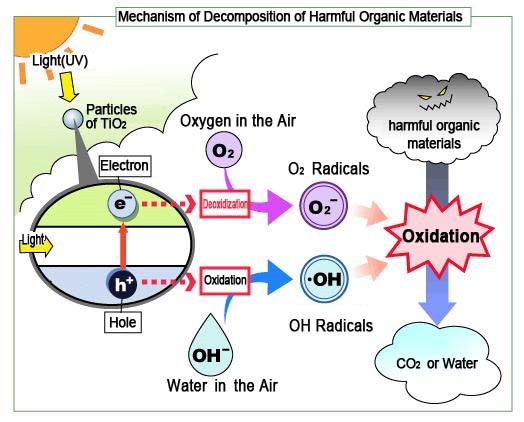
(1)Decomposition of harmful organic materials
When TiO2 is exposed to UV (Ultraviolet rays), it makes electrons and holes, which means TiO2 is ionized. Electron and holes react with oxygen and water in the air, and make O2 and OH2 radicals. These radicals decompose harmful organic materials.
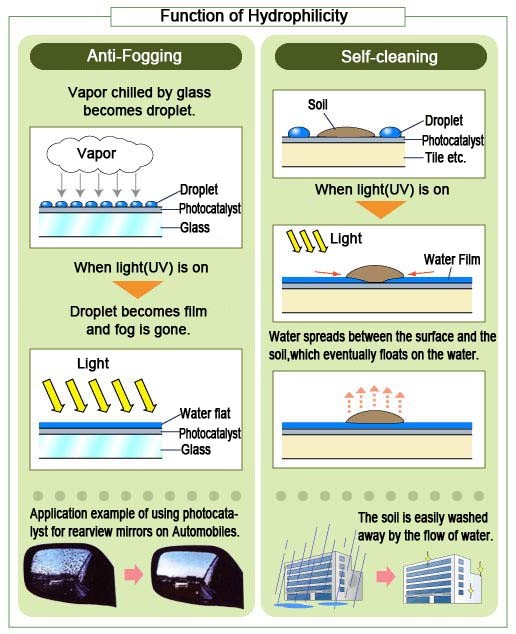
(2)Hydrophilicity
When TiO2 is exposed to UV, the surface becomes hydrophilic. Hydrophilicity prevent from fogging of glasses and mirrors.
In addition, soils on the surface can be easily removed with water(Self-cleaning).
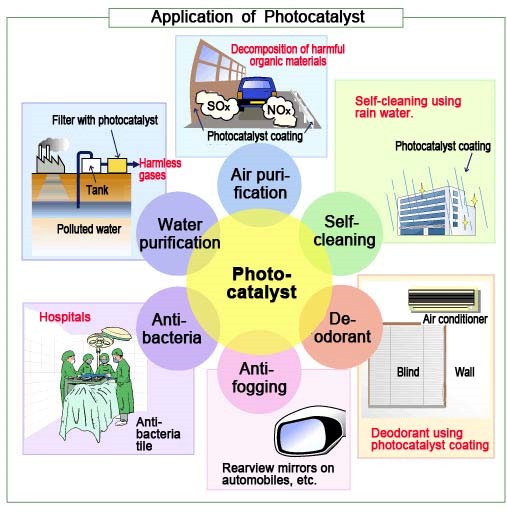
3.Application of photocatalyst
Using photocatalyst technology, there are a lot of application as follows. However, most of the photocatalyst needs UV to make reaction at the moment. To expand the application of photocatalyst, many of Japanese companies are developing new photocatalyst which can be react even with normal light(radiant energy)